day10
栈和队列
讲解链接:栈和队列
std::stack<int, std::vector<int> > third; // 使用vector为底层容器的栈
std::queue<int, std::list<int>> third; // 定义以list为底层容器的队列
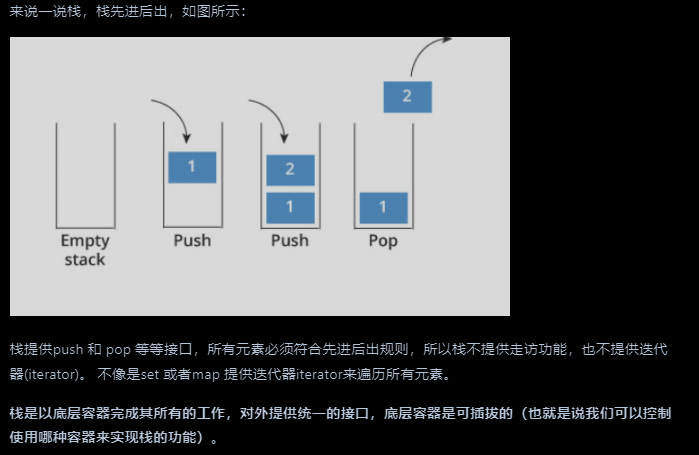
Q:C++中的stack是容器么?
A:不是,其属于容器适配器(container adapter),
Q:我们使用的stack是属于哪个版本的STL?
A:三个最普遍的STL版本

我们使用的是SGI STL版本
Q:我们使用的STL中stack是如何实现的?
A:
232.用栈实现队列
题目链接:232. 用栈实现队列
解题思路:使用两个栈,对于添加元素直接push即可,移除元素时候需要检查第二个站是否为空,如果为空,将第一个栈的所有元素推入到第二个栈同时删除第一个栈的元素。最后删除并返回第二个栈的栈顶元素。
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
MyQueue() {
}
// 添加元素到队列
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
// 移除元素
int pop() {
// 只有当stOut为空的时候,从stIn里面导入全部数据
if( stOut.empty()){
while( !stIn.empty() ){
// 从stIn导入数据直到stIn为空
// 推入栈顶元素
stOut.push(stIn.top());
// 删除stIn中的元素
stIn.pop();
}
}
// 删除并返回stOut中的元素
int result = stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return result;
}
int peek() {
// 使用 pop()函数
int res = this->pop();
stOut.push(res);//pop函数弹出了栈顶元素,再添加回去
return res;
}
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
225.用队列实现栈
题目链接:225. 用队列实现栈
解题思路:用一个队列实现栈,push元素直接push就好,pop元素时候,先获取队列的大小,然后循环将队头元素Push进队列,循环size-1次,同时弹出该元素,最后记录队头元素,删除队头元素并返回。
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
int pop() {
// 获取队列的大小
int size = que.size();
size--;
while(size--){//将队列的头元素循环添加到队列中,循环size-1次,同时弹出头元素。
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front();//记录头元素
que.pop();
return result;
}
int top() {
return que.back();
}
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
两个队列实现,相当于queue2作为备份作用
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que1;
queue<int> que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que1.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将que1 导入que2,但要留下最后一个元素
que2.push(que1.front());
que1.pop();
}
int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要返回的值
que1.pop();
que1 = que2; // 再将que2赋值给que1
while (!que2.empty()) { // 清空que2
que2.pop();
}
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que1.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que1.empty();
}
};